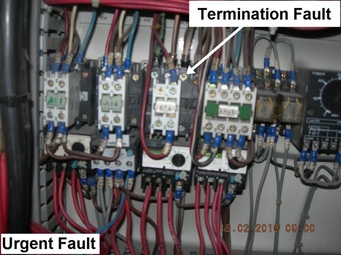
What Is Thermal Imaging?
Thermal Imaging is a process of taking a picture and mapping the temperatures at each point in the picture.
How Does Thermal Imaging Map These Temperatures?
Imagine we could layer the picture or thermograph into two layers – a top and a bottom layer.
The bottom layer of the Thermal Image is divided up into tiny square or rectangular pieces called an array. Each tiny rectangle has a temperature component so the operator can easily determine any hot spots or cold spots within the array.
The top layer of the Thermal Imaging array is the part we see when we look though the viewfinder. It is possible to set the range of the temperature so that the highest temperature being viewed is white and the bottom temperature is black. The intermediate temperatures are different shades of grey. This is called a temperature scale. We can chose to assign any colour to any temperature within the temperature scale and the colours we use to map the picture are known as false colour. Thermographers generally use an Iron Scale but there are 6 commonly used false colours.
Thermal Images are accurate to less than one tenth of a degree. It is often more important to map temperature differences than the absolute temperature.
The bottom layer of the Thermal Image is divided up into tiny square or rectangular pieces called an array. Each tiny rectangle has a temperature component so the operator can easily determine any hot spots or cold spots within the array.
The top layer of the Thermal Imaging array is the part we see when we look though the viewfinder. It is possible to set the range of the temperature so that the highest temperature being viewed is white and the bottom temperature is black. The intermediate temperatures are different shades of grey. This is called a temperature scale. We can chose to assign any colour to any temperature within the temperature scale and the colours we use to map the picture are known as false colour. Thermographers generally use an Iron Scale but there are 6 commonly used false colours.
Thermal Images are accurate to less than one tenth of a degree. It is often more important to map temperature differences than the absolute temperature.
Thermal Imaging Benefits
• Reduced downtime due to equipment failure
• Reduced repair costs
• Reduced risk of electrical fires
• Protection of your assets
• Reduced Insurance premiums (in some instances)
• Peace of mind
• Reduced repair costs
• Reduced risk of electrical fires
• Protection of your assets
• Reduced Insurance premiums (in some instances)
• Peace of mind